This article serves as a summary and notes translated into Spanish of what I consider the Leaders of Learning course bases, from Harvard University, where Professor Elmore proposes 4 modes of leadership divided into several dimensions, which form the quadrant of the 4 Leadership Styles.
In addition, this quadrant is also used throughout the course to analyze and study other basic competencies for learning, such as learning itself, and organization. Thus, you will be able to find in this blog summaries of the 4 Learning Styles and the 4 Organization Styles proposed on this same scheme.
If these bases serve you, remember that you can assess for yourself whether or not to purchase the complete course at: https://www.edx.org/course/leaders-of-learning
Post content:
Theory of the 4 Modes of Leadership – Richard Elmore
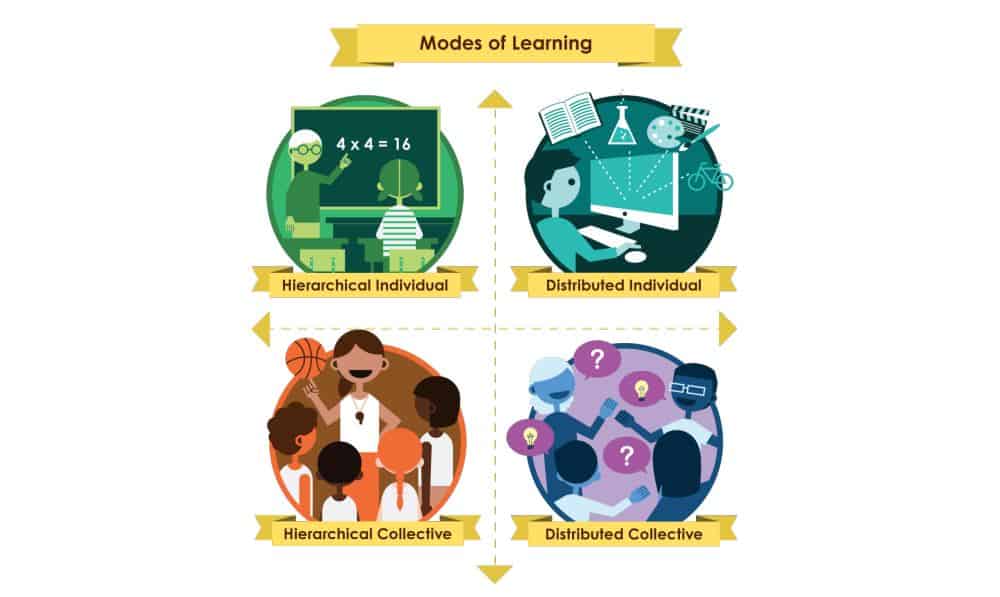
Hierarchical Individual

Among the different leadership styles, in the Hierarchical Individual:
Expectations
Being a successful leader in a hierarchical individual learning environment means incorporating the external requirements of a governing institution (often the state or federal government) into the work and practices of the organization.
Knowledge and skill requirements
A hierarchical individual learning environment typically values a leader who:
- Successfully manages relationships between superiors and subordinates.
- Focuses the organization and its students on clear performance objectives.
- Directs the human and material resources of the organization at the service of those
performance objectives. - Builds and maintains stable relationships with students and their families based on high
expectations.
Hierarchical Collective

Among the different leadership styles, in the Hierarchical Collective:
Expectations
Being a successful leader in a hierarchical collective learning environment means leading according to the requirements of an external authorizing environment, while promoting and applying the learning community's own norms, values, principles and practices.
Knowledge and skill requirements
A hierarchical collective learning environment typically values a leader who
- Articulate and model the organization's key values.
- Incorporates external requirements into the specific values and practices of the community.
- Builds and maintains stable relationships with students and their families based on standards
specific norms of this learning community.
Individual Distributed

Among the different leadership styles, in the Individual Distributed:
Expectations
Being a successful leader in a distributed individual learning environment means articulating an engaging vision of learning that adapts to the needs, preferences, and dispositions of learners.
Knowledge and skill requirements
A distributed individual learning environment typically values a leader who
- Respond to students' needs and interests and consider how they will change over time.
- Don't be afraid to embark on new business adventures.
- Build and inspire a team of collaborators with diverse knowledge and skills.
- Mobilizes human and material resources to respond to the needs of students.
- Closely monitors students' engagement, interest, and connections to the
learning.
Distributed Collective

Among the different leadership styles, in the Individual Distributed:
Expectations
Being a successful leader in a distributed collective learning environment means identifying and supporting the common values, beliefs, and goals that unite the learning community.
It often means being open to sharing ownership of an educational vision with the community.
Leadership knowledge and skills
A distributed collective learning environment typically values a leader who:
- Inspires individuals and organizations with common interests to network
in network. - Recognizes the shared values of the community and articulates them within the community and the
world in general. - Identifies community members' resources and motivates them to share them.
- Brings resources from the outside world into the community, while maintaining the
community norms and standards.
